We all want to lead healthy and fulfilled lives. However, certain medical conditions can make this dream seem almost challenging. These medical conditions can sometimes be minor and will only minimally affect our daily lives. Such medical conditions will usually also require treatments that are simple and sometimes even home-based. There are some diseases though, that are considered severe, life-threatening, and debilitating if not treated immediately. One such medical condition is known as Hepatic Encephalopathy. But what is this medical condition? What are the signs of hepatic encephalopathy and, and how can it be treated and diagnosed? We answer that question in this article, so if you want to know more, read on!
Hepatic Encephalopathy: A General Overview
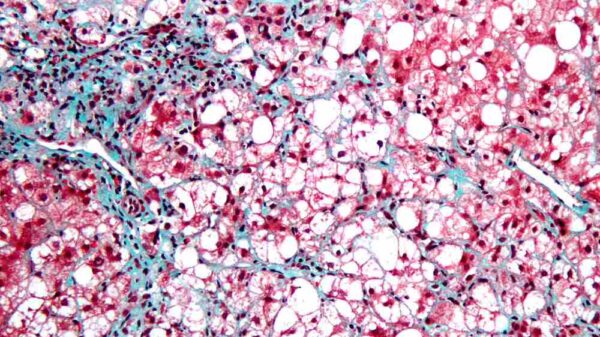
Hepatic Encephalopathy is a condition that occurs when a liver disease results in the decline of the functions of the brain. When this happens, the toxins in the blood can no longer be removed by an impaired and ineffective liver. That can lead to the bloodstream having an accumulation of toxins, which can then lead to damage to the brain Hepatic Encephalopathy can either be chronic or long term or it can be acute or short term. For some, Hepatic Encephalopathy can lead to unresponsiveness and eventually comatose.
The Different Types of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Acute hepatic Encephalopathy can develop due to liver disease that is severe and can occur to people mainly with the following conditions:
- Acute Fulminant Viral Hepatitis: This is a form of hepatitis that is viral and quite severe and can have a sudden onset.
- Toxic Hepatitis: This kind of hepatitis can be due to exposure to supplements, drugs, chemicals, or alcohol.
- Reyes’ syndrome: This condition is a rare and serious one and is often seen and diagnosed in kids. It can lead to sudden inflammation and swelling of the brain and the liver.
Acute Hepatic Encephalopathy may also be an indication that the liver is already failing to function. On the other hand, Hepatic Encephalopathy that is chronic can either be recurrent or permanent. Individuals suffering from recurrent Hepatic Encephalopathy will have several episodes of the said condition. These individuals will also need regular management and treatment to prevent the symptoms from progressing any further. These recurrent cases will commonly be observed in people that have liver scarring, and severe cirrhosis.
The Symptoms and Signs of Hepatic Encephalopathy
The signs and symptoms of Hepatic Encephalopathy will vary based on the liver damage’s underlying cause. Some of the signs and symptoms for Hepatic Encephalopathy that is considered moderate can include a breath odor that is sweet or musty, poor judgment, forgetfulness, confusion, loss of hand movements such as handwriting, poor concentration, changes to the personality, and difficulty thinking.
For the severe forms of Hepatic Encephalopathy, some of the signs and symptoms may include slow movements, shaky hands, confused speech, fatigue, personality changes, seizures, anxiety, lethargy, drowsiness, and confusion. Patients are advised to seek immediate emergency attention if they observe the said symptoms of severe Hepatic Encephalopathy, as these can be a risk for slipping into a coma.
What are Hepatic Encephalopathy’s Possible Causes?
Currently, the specific cause of Hepatic Encephalopathy is still unclear. However, experts theorize that it all starts with toxin accumulation or buildup in the blood. It can happen when there is a failure in the part of the liver to have the toxins broken down properly. The liver is responsible for the removal of chemicals that are toxic to the body, such as ammonia. These toxins are the result of leftovers of metabolized proteins that have been broken down to be used by the different bodily organs. The kidneys then convert these toxins into substances that are safer before having them excreted or removed via the urine.
Once there is damage to the liver, it can no longer have the toxins filtered out, which can then lead to the toxins building up and accumulating in the bloodstream. This toxic buildup can harm the brain and also the nerves and the organs. Several conditions can trigger Hepatic Encephalopathy, and these are imbalances in electrolytes, certain medications that suppressed nervous system, eating increased amounts of protein, medications that can have the immune system suppressed, recent trauma or surgery, low levels of oxygen or hypoxia, dehydration, problems with the kidney, and pneumonia and other similar infections.
Diagnosing Hepatic Encephalopathy
Fortunately, several different tests can help medical professionals diagnose Hepatic Encephalopathy. These are:
- Blood test: To check the platelets, red blood cells, and the white blood cells, a complete blood count may be conducted. A red blood cell count that is low can be an indicator that there is a lack of oxygen or loss of blood.
- Imaging Tests: MRIs or CT scans may be used to check the patient for any brain abnormalities or bleeding in the head
- Tests to Check Liver Function: These kinds of tests will check for the levels of enzymes and an increased level of these substances can indicate the liver is under stress or may already be damaged.
Patients are advised to tell their healthcare partner about their family history and any symptoms they may be experiencing as these can be sufficient in the diagnosis of Hepatic Encephalopathy.
Possible Treatment Options for Hepatic Encephalopathy
Some options for the treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy will depend mostly on the underlying cause and severity of the medical condition. People will most likely have to reduce their protein intake. That means that a dietician may need to create a diet plan for the individual as protein is crucial for the overall health of the individuals. Some of the food items that are protein-rich and should, therefore, be avoided are fish, eggs, red meat, and poultry.
Doctors can also prescribe certain medications, such as lactulose and antibiotics. Severe cases may also lead to possible liver transplants. People need to discuss this option with their doctor to check on their eligibility for liver transplantation.